BCG aftercare
Last edited: 16/9/2025
Alternative formats
This leaflet is available in:
The BCG vaccination
The Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination has been administered to help give protection against Tuberculosis (TB). The BCG is provided by AJ Vaccines and is licensed for use in the UK.
The nurse should have explained the points below before the BCG vaccination was given. If you have any questions please ask at your appointment or contact us.
- It’s a live vaccine containing a weakened form of the bacteria that causes TB. Because it is weakened it doesn't actually cause TB but helps people develop immunity against it.
- It’s given under the skin and the body slowly absorbs it.
- The BCG vaccine should not make you feel unwell.
- Following changes in advice from Public Health England regarding live vaccines, the BCG can now be given at any time. This means it can be given before or after rotavirus, live attenuated influenza vaccine, oral typhoid vaccine, yellow fever, varicella, zoster, MMR and tuberculin skin testing. A four week interval does not need to be observed.
- If further vaccinations are given, they should not be given in the same arm for a period of three months.
- The BCG vaccination is only given once. Even if no scar develops, we do not re-vaccinate.
- We advise that you do not become pregnant within three months of receiving the BCG vaccination.
- We recommend that you should not come into contact with anyone with active TB or travel to a country with a high level of TB during the first six weeks after vaccination. This is because you will not be fully protected.
The injection
The injection is given just under the skin of the left upper arm (Deltoid). The vaccination usually leaves a white mark under the skin.
This mark will disappear a few hours after it has been given. Between two and six weeks later a small lump where the injection was given will appear. It can be up to the size of a five pence piece. It may ooze and form a scab. This is quite normal but may take several months to heal.
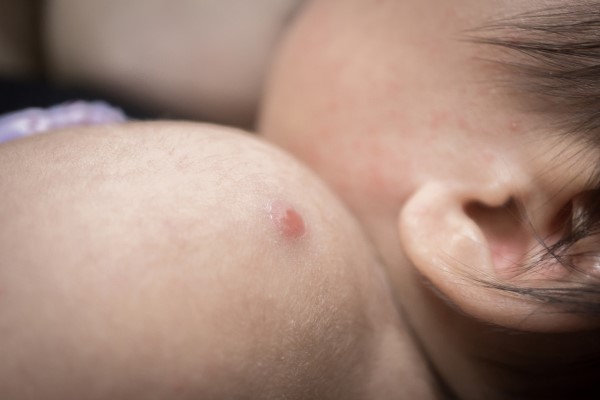
After care
- Keep the area clean.
- No creams, lotions or plasters should be used on the area. Only use a plaster if you are going swimming.
- If it oozes on to clothing a small dry woven dressing may be used.
- The sore should gradually heal over to leave a scar on the arm.
If you are worried about the vaccination reaction please contact the Tuberculosis (TB) Nursing Team or out of hours, NHS 111.
Contact us
Contact your GP for advice or contact our service on:
0300 123 1430
kentchft.tbadmin@nhs.net
Monday to Friday, 8am to 5pm
This information should only be followed on the advice of a healthcare professional.
Do you have feedback about our health services?
0800 030 4550
Text 07899 903499
Monday to Friday, 8.30am to 4.30pm
kentchft.PALS@nhs.net
www.kentcht.nhs.uk/PALS
Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS)
Kent Community Health NHS Foundation Trust
Trinity House, 110-120 Upper Pemberton
Ashford
Kent
TN25 4AZ
![]()
Donate today, and help the NHS go above and beyond. Visit www.kentcht.nhs.uk/icare
If you need communication support or this information in another format, please ask a member of staff or contact us using the details above.
